 Politics
Politics






N. Haitov
Only those whose hearts want to fly have wings...


W. Stone
Every great dream begins with the dreamer.


E. Casey
Dreams are today's answers to tomorrow's questions.


N. Hill
A person can achieve anything if he believes in it.

More about civic education in our life - BULGARIA
 Politics
Politics Scheme
Scheme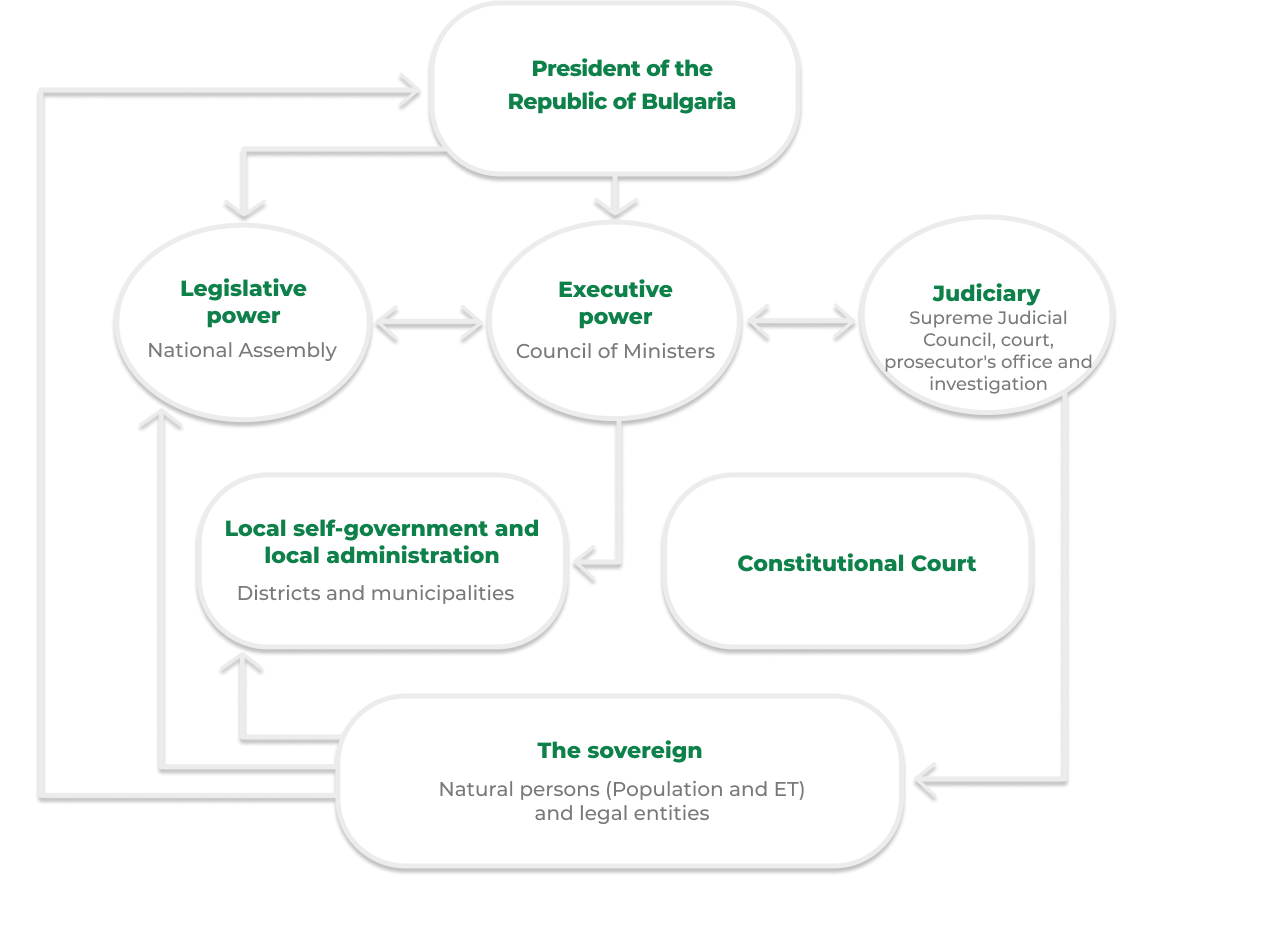
Legislative Power is exercised by the parliament of the Republic of Bulgaria - the National Assembly. It consists of 240 representatives, elected every four years. The National Assembly is responsible for adopting laws, amending the constitution, approving the budget, and overseeing the executive branch.
Executive Power is exercised by the President of the Republic of Bulgaria, who is the main figure in the state and the government. The President is responsible for representing the state internationally, signing and promulgating laws, dissolving the National Assembly, and other important functions. The government, composed of ministers, manages the daily tasks of the state and implements the policies outlined in the governance program adopted by the parliament.
Judicial Power includes the Constitutional Court, the Supreme Court of Cassation, appellate courts, and general courts. Judges are independent and inviolable in performing their functions and are responsible for applying the law and resolving disputes within the legal system of Bulgaria.





 Society
Society
 Institutions
Institutions
1. State Governance and Legislation:
National Assembly: Legislative body that adopts, amends, and repeals laws, conducts parliamentary control, and formulates the political will of the nation.
Government: Executive body responsible for the administration of the country, implementation of policies, execution of laws, and decision-making on important issues.
Ministries: Responsible for administration in various sectors such as the economy, education, healthcare, transportation, agriculture, and others.
2. Judiciary:
Supreme Cassation Court: The highest judicial instance that exercises control over the correct application of laws and makes decisions on cassation appeals.
Judicial instances: Include administrative, district, appellate, and supreme courts, which decide on civil and criminal matters.
3. Central Bank:
Bulgarian National Bank (BNB): Responsible for managing monetary policy and financial stability, controlling the banking system, and ensuring the functioning of payments.
4. Regulatory Institutions:
Commission for Protection of Competition (CPC): Responsible for ensuring competition protection and preventing unfair market practices.
Energy and Water Regulatory Commission (EWRC): Responsible for regulating the energy and water sector, including establishing tariffs and controlling suppliers.
Financial Supervision Commission (FSC): Responsible for overseeing financial institutions such as stock exchanges, banks, insurance, and pension companies.
5. Local Self-Government:
Municipalities: Represent the lowest level of local self-government and ensure the management of local issues and services within their territory.
Municipal Councils: Elected by citizens and make decisions on local issues, budgets, and the development of the municipality.
6. Education:
Ministry of Education and Science: Responsible for developing and implementing educational policies, standards, programs, and curricula.
Universities and Higher Education Institutions: Offer higher education and engage in scientific activities in various fields.
 Informational Pages
Informational Pages



 Test
Test







 Civic Education Lessons
Civic Education Lessons
 Several examples of civic education lessons:
Several examples of civic education lessons:
- Discussing the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and its significance.
- Analyzing specific cases of rights and freedoms violations and ways to protect these rights.
- Creating posters or brochures that inform about the importance of human rights and freedoms.



 Youth Engagement in Action
Youth Engagement in Action
 Benefits of Youth Engagement
Benefits of Youth Engagement
1. Improvement of Civic Skills:
Youth engagement helps young people develop and enhance important civic skills such as communication, leadership, teamwork, negotiation, and problem-solving.
2. Development of Self-Esteem and Confidence:
When youth engage in addressing social issues and actively work towards their resolution, they feel confident in their ability to make a positive impact on the world around them.
3. Understanding of Social Issues:
Youth engagement provides an opportunity for young people to understand and assess social issues that affect their communities and the world as a whole.
4. Building Connections and Networks:
Youth engagement allows young people to meet and work with other youth and adults who share similar interests and goals.
5. Influence on Public Decisions:
Youth engagement provides young people with the opportunity to be part of the process of making public decisions and to influence them.
 Opportunities for Youth Engagement
Opportunities for Youth Engagement
Volunteering: Youth can participate in volunteer programs and projects addressing various social, environmental, or educational challenges. This may include working with homeless people, assisting children in need, environmental conservation, and more.
Social Projects: Youth can initiate and organize their social projects aimed at solving specific problems or assisting those in need. This may involve fundraising, conducting awareness campaigns on social issues, creating school or community gardens, and similar initiatives.
Political Engagement: Young people can engage in political processes and express their views and ideas. This includes participation in youth organizations, volunteering in political campaigns, creating petitions, participating in public discussions, and more.
Technology and Media: Youth can use technology and media to convey their messages and influence public opinion. They can create blogs, video materials, websites, or engage in online campaigns and movements.
 Media Literacy
Media Literacy
1. Understanding Media Sources: Media literacy includes analyzing and evaluating various media sources. This involves understanding different media types, such as news websites, television channels, and social networks. Students should be taught how to recognize trusted and reliable sources that provide verified information.
2. Critical Thinking and Analysis: Media literacy develops critical thinking and the ability to analyze media messages. Students should be taught how to question information, fact-check, detect manipulations, and form their own informed opinions.
3. Recognizing Fake News: Nowadays, fake news and misinformation are widespread. Youth should be trained to recognize and debunk fake news. They need to learn how to verify sources, confirm information from multiple independent sources, and be cautious of signs of manipulation and deception.
4. Ethics and Responsible Media Use: Young people must understand and accept their responsibility as media consumers. They should be taught to share information from reliable sources, refrain from sharing fake news, and approach media with common sense and ethics.
 Assessment of Youth Activity Impact
Assessment of Youth Activity Impact
 Test
Test







 Life, Work, Travel in the EU
Life, Work, Travel in the EU

 What Does the EU Do for Its Citizens?
What Does the EU Do for Its Citizens?

4. Education and Youth Mobility: The EU encourages educational programs and youth mobility, such as the Erasmus+ program. This provides opportunities for students, teachers, and young people to study, work, and live in different EU member states, expanding their knowledge and experience.
5. Financial Support: The EU provides financial support through various funds and programs. This includes support for entrepreneurship, scientific research and innovation, regional development, agriculture, and social inclusion.

 What Are the European Instruments?
What Are the European Instruments?
1. EU Treaties: These are the legal foundations of the EU, establishing the basic principles, goals, and rules for the functioning of the EU. The most important treaties are the Treaty on European Union (TEU) and the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union (TFEU).
2. European Commission: The Commission is the executive body of the EU and is responsible for proposing and implementing EU legislation, managing the EU budget, and representing EU interests on the international stage.
3. European Parliament: The Parliament is the legislative body of the EU and represents the citizens of the EU. It has the authority to adopt, amend, and approve EU legislation, supervise the work of the European Commission, and participate in shaping EU policies.
4. Council of the EU: The Council is the body representing the governments of the EU member states. It participates in formulating EU legislation, jointly with the European Parliament, and has the power to make decisions on important EU issues.
 Documents and Publications of the Erasmus+ Program
Documents and Publications of the Erasmus+ Program
1. EU Treaties: These are the legal foundations of the EU, establishing the basic principles, goals, and rules for the functioning of the EU. The most important treaties are the Treaty on European Union (TEU) and the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union (TFEU).
2. European Commission: The Commission is the executive body of the EU and is responsible for proposing and implementing EU legislation, managing the EU budget, and representing EU interests on the international stage.
3. European Parliament: The Parliament is the legislative body of the EU and represents the citizens of the EU. It has the authority to adopt, amend, and approve EU legislation, supervise the work of the European Commission, and participate in shaping EU policies.
4. Council of the EU: The Council is the body representing the governments of the EU member states. It participates in formulating EU legislation, jointly with the European Parliament, and has the power to make decisions on important EU issues.
 Test
Test

